WORK IN PROGRESS
This section is progress, we hope to provide a more comprehensive introduction to modeling with Quetzal soon. Quetzal Library is an opensource python toolbox used to build static macroscopic transport models from scratch. It provides a flexible object model to handle modeling attributes and many algorithms used for demand and assignment models.
We sketch out at broad strokes out in broad strokes the mathematical concepts behind Quetzal's architecture and algorithms. Yet we do not breakdown in detail these concepts and keep the focus on the library itself.
More details about static macroscopic modeling can be found in the great book that inspired most of Quetzal's implementation. de Dios Ortúzar, J., & Willumsen, L. G. (2024). Modelling transport. John wiley & sons
4 Step Structure | Work In Progress
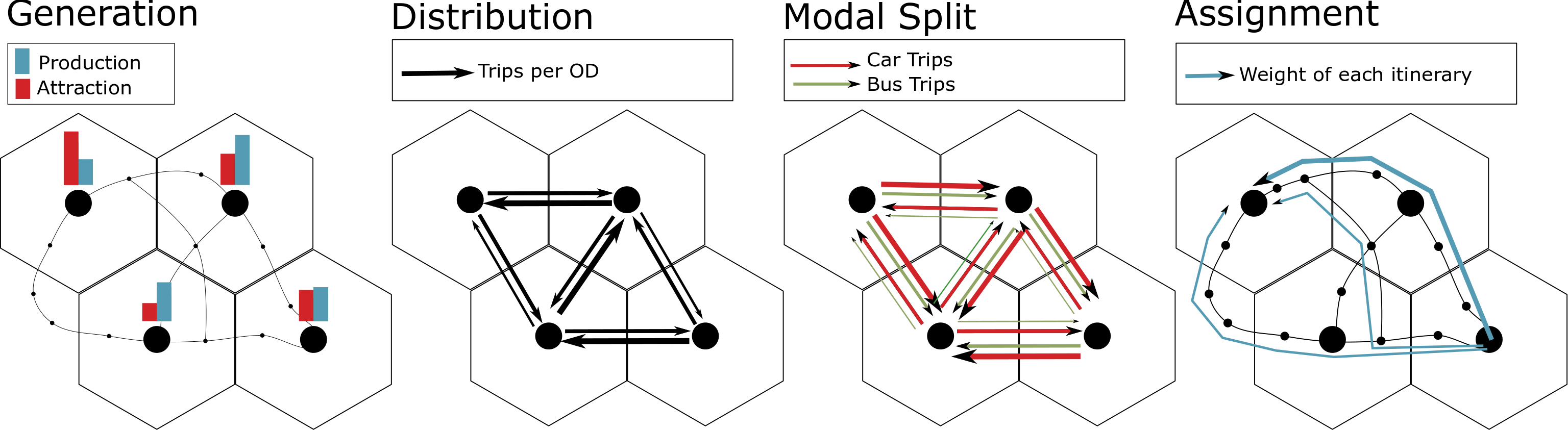
Quetzal was inspired by the classical 4 step transport modeling and provides algorithms
- In the generation, zonal data such as number of households and jobs is used to assess the volume of outgoing and ingoing trips of each zone. These trips are respectively called productions and attractions.
- In the distribution, the productions and attractions are balanced and the destinations of the outgoing trips of each zone are chosen.
- In the modal split , the the volume of passenger of each Origin-Destination (OD) pair is split between the available modes.
- In the assignment, the relevant itineraries of each OD pair are enumerated and the users are shared amongst those paths.
🐦 A thought on the order of the steps
- The classical sequence of the four steps is based on :
- Data workflow constraints e.g., the outputs of the generation are used for the distribution
- Our understanding of the decision process and what is more important to us
- A calibration order that minimizes the need for feedbacks and saves time
- It is flexible though:
- The travel times generated in the assignment are used in the upstream steps of distribution and modal split
- Two or more steps can be integrated in order to model our choices more accurately.
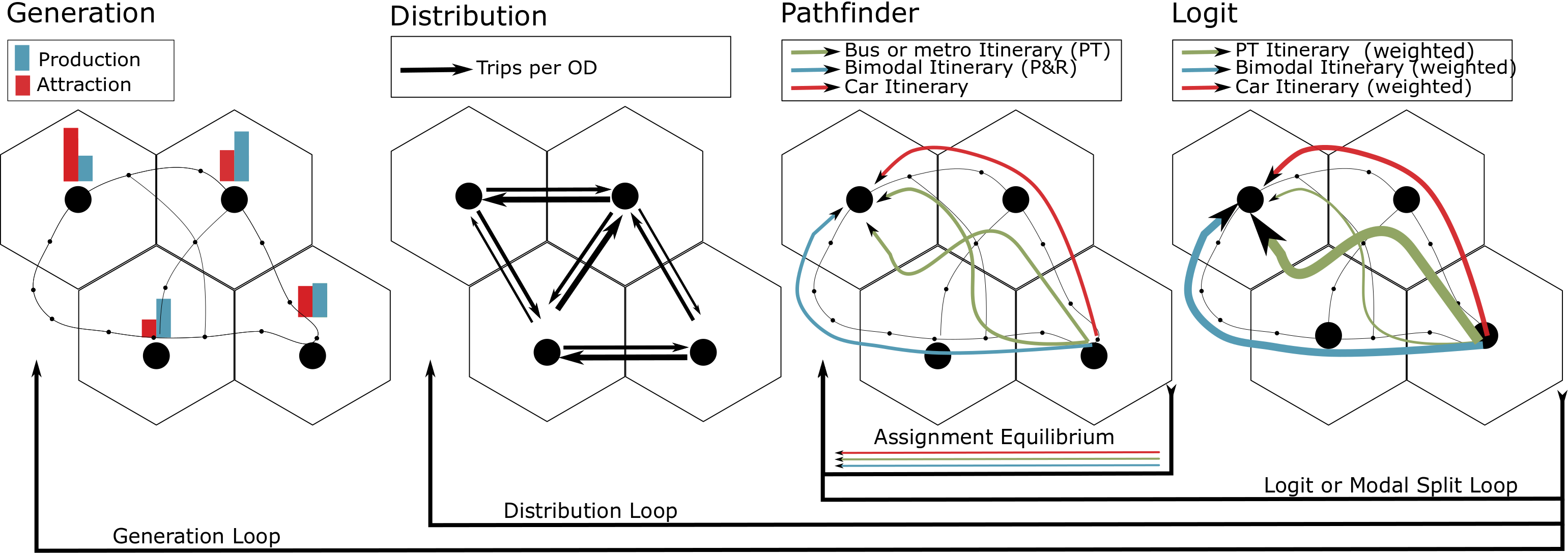
- Although Quetzal provides the tools to build a standard four-stage model, we often use another framework to better model multi-modality and ensure consistency between the modal split and the assignment
- Generation and distribution remain the same
- The pathfinder step enumerates all the paths of the different modes, public and private
- The logit step does the modal split and the weighting of the different itineraries
- Retroaction loops are used between the steps
Assignment | Work In Progress
Optimal Strategies
- Optimal Strategies can be established toward the destinations
- It a set of relevant line to board at each station and associated alighting stations
- The path is not known beforehand but is built along the journey of the traveler
- The expected time of arrival is better than the better sequence of lines yielded by the shortest path algorithm run in a frequency-based graph
- The assignment on each link is derived from the deterministic strategies
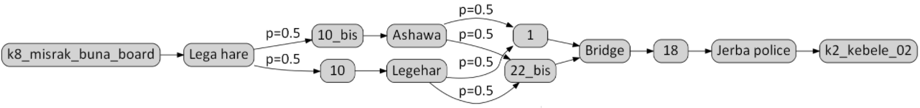
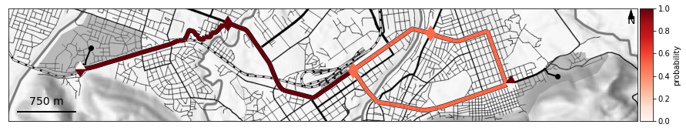 On this complex example in Dire Dawa (Ethiopia):
On this complex example in Dire Dawa (Ethiopia): - users start from Misrak Buna in the east and go to Kebele 2 in the west
- Then they wait in Lega Hare, for the 10 or 10bis to stop and board the first one.
- Then, those who board line 10 alight in Legehar and the users of line 10 bis alight in Ashawa.
- Both line 1 and line 22bis stop at Ashawa (first stop) and Legehar. Our users will board the first of these line to stop at their station.
- Once they are in line 1 or 22bis, they will alight in Bridge to board the line 18 and alight at Jerba Police then walk to their final destination.
Connection Scan Algorithm
- Connection Scan Algorithm is a timetable-based pathfinder
- Provides a departure time vs arrival time pareto-optimal (non dominated) set of paths
- A path dominates another if it has both a later departure time and an earlier arrival
- Can be run in public transport subgraphs (pruned graphs) to yield non pareto optimal itineraries
- The route choice can be integrated with the mode choice and the time-of-day choice in a nested logit by discretizing the origin-destination matrix in origin-destination-wished departure time matrix

Iterative Pruning Algorithm | Work In Progress
Quetzal Iterative Pruning approach was inspired by applications such as Google Maps or CityMapper. They yield a broad variety of public transport path. The algorithme could be summarized with the following sequence :
- Search the best path
-remove a route from the original transit data so that the best path is no longer possible - Search the best path -remove another route so that neither the best nor the second best are possible
- Search the best path
- remove all the buses
- Search the best path
- remove the subway and the trains … etc. At each iteration only the best path of a transit dataset is returned
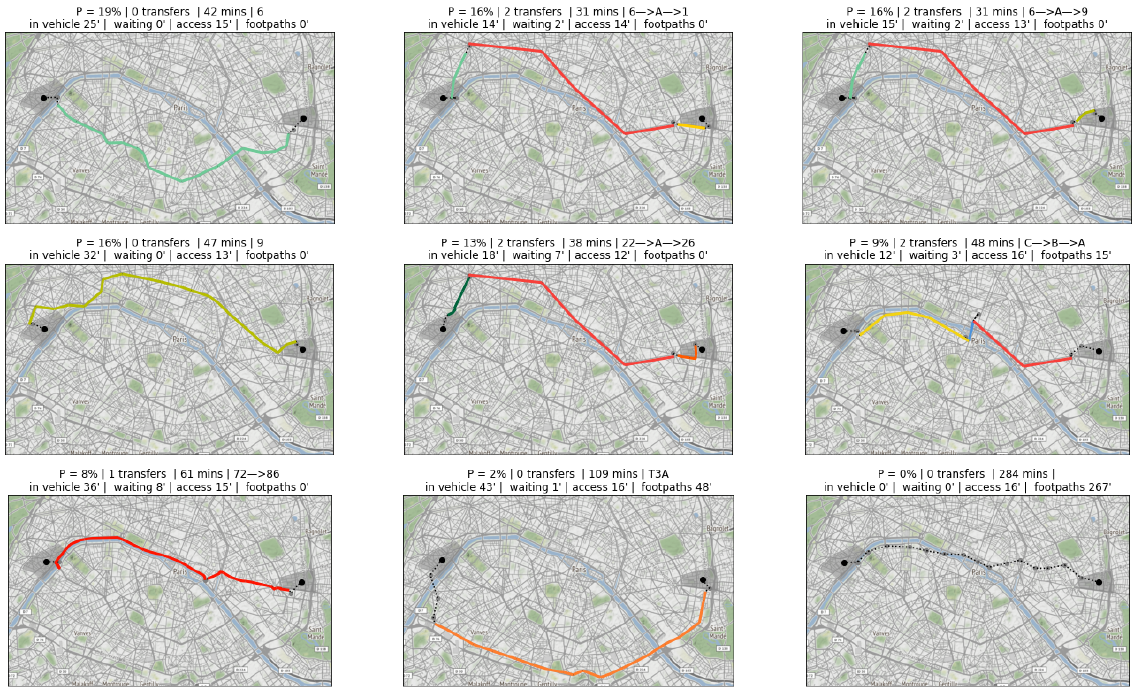
- remove the subway and the trains … etc. At each iteration only the best path of a transit dataset is returned